Data lifecycle management is a crucial practice for any successful business, whether it is a large or small business.
Small businesses let “small” documents slip through the cracks, rather adequately filing them away which can lead to deleted or missing files and data can end up in the wrong hands.
With the right data lifecycle management practices and planning, your business will know how to manage the data safely & efficiently from the point of creation to the point of deletion.
Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) combines a business and technical approach to improving database development (or acquisition), delivery, and management.
The scope of Database Lifecycle Management is intended to make all the processes that make up the lifecycle more predictable and visible. The objective is reducing costs and increasing quality while encouraging innovation & cooperation between the different teams.
It also helps to find out the ways of ensuring that the right things happen at the right time. Along with ensuring that every team has the best and correct information with them.
Data lifecycle management is beneficial to any business storing and utilizing internal data as well as consumer data.
Without proper data lifecycle management practices, it’s inevitable that your business will misplace or be unable to locate a necessary file or data.
With the right data lifecycle management practices in place, your business can mitigate the risk of data deletion, loss, and breaches.
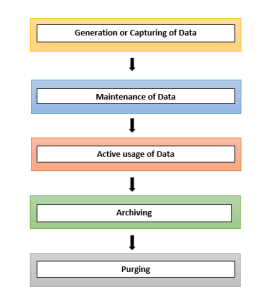
Data management experts often identify 5 or more stages in the data lifecycle. Here are 5 stages:
In this phase, data comes into an organization, usually through data entry or acquisition from an external source.
In this phase, data is processed before it is used.
In this phase, data is used to support the organization’s objectives and operations.
In this phase, data is removed from all active production environments. It is no longer processed, used, or published but is stored in case it is needed again in the future.
In this phase, every copy of data is deleted which is already archived.
Defining your data types
Your organization likely handles many different types of documents and files. However, you’ll need to distinguish the types of data you manage.
For example, Customer or patient data will need to be handled differently as compared to accounting data.
Identifying the type of data you store and utilize is the starting point for outlining how to manage each kind.
Losing data because it’s unsearchable is an easily preventable data lifecycle management failure.
Your organization should abide by a simple, yet thorough file naming structure that will allow anyone within your organization to find the data they need in seconds.
Any file that lives on a physical storage device or computer is vulnerable to loss.
While loss and deletion can also occur due to physical damage, virus, natural disaster, and many other threats. However, the most common data loss scenarios can be related to human error too.
As you define your data lifecycle management practices, you’ll want to invest in a reliable backup solution to backup all of the data in your system.
To protect your data adequately from loss and deletion, it’s essential to invest in a backup tool that will help in backing up the files of your company.
With a solution like this, your organization will have the ability to retrieve any file at any time, eliminating permanent data loss.
Creating a data archive policy will help your employees in deciding how to manage data that is no longer in use but it needs to be retained.
Since your strategy will vary depending on the type of data involved. A go-to-option is to develop a policy that will provide you and your employees the guidelines to help make better decisions.
Depending on the type of data involved, you may be able to elect this infrequently used data to move into your storage archive.
Moving seldom-used data into an archive can clear up storage space on the devices you use daily and accelerate processing speeds to make your business run faster.
Just as you’ll need an archive policy to help your organization determine to archive best practices per data type, you’ll also need a data deletion policy to do the same.
It’s essential to outline data destruction guidelines for each type of data so that you’re correctly deleting the data that you no longer need.
Having clear-cut guidelines is the only way to get your entire organization on board. And, participating in your new data lifecycle management structure.
Once you’ve defined the processes for handling data storage, management, backup, archiving, and deletion, you’ll want to add these up to your data management policy.
The policy should be shared with everyone in your organization so that they’re aware of the new process.
You may want to assign a person for your new data management policy that can keep your organization on track with compliance. Further, guide less tech-savvy users on how to implement these new practices so that they’ll stick.
By implementing these best practices, you can be assured that your data will remain safe.
You can immediately check off a highly significant step in building your internal data lifecycle management practices by instituting an automatic and continuous backup solution.
Recommended For You:
What is Email Deliverability? Here are 5 Ways to Improve Email Deliverability
10 Best Inventions in the Last Decade that Changed the Technology Sector

