Unlike a biological virus, malware is continuously adopting new technologies and is evolving at a rapid pace.
IT Security teams keep developing antivirus software to keep their systems safe by detecting and removing malware, but it still affects more computer systems than ever before.
In May 2019, Microsoft recently revealed a Windows security vulnerability that could see a “wormable” attack that transmits from one system to another.
This could be as devastating as WannaCry was in 2017. Microsoft also said that nearly 1 million systems could get attacked if not updated to their latest security update.
Malware infections have risen in the past 5-7 years. Hackers use malware as their primary tool to steal users’ data.
Malware is likely to increase in the future as most users are now connected to the Internet and rely on websites for banking, education, etc.
It keeps transmitting information from one website to another, increasing the risk of malware infecting your device or system.
New threats are always in development to stay ahead of the antivirus developers to gain users’ data.
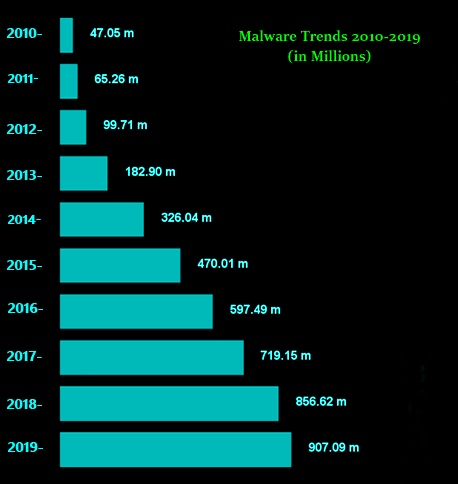
In the above graph, we can see the malware trends (in millions) from 2010 to 2019. We can also see that malware attacks are increasing with the increase in tech-savvy users and their increasing dependency on online services.
Let’s look at some malware and see how it affects the cyber world.
Social Engineering – Social engineering remains a devastating threat, where cybercriminals trick the user into revealing sensitive information.
WannaCry—It was identified in 2017 and affected almost 400,000 computers with older OSes than Windows 7, and their security patches were not updated.
Affected giants included FedEx from the United States, NHS from the UK, and Telco from Spain.
NotPetya – It also targeted an outdated window’s operating systems just after WannaCry. This malware cracks passwords of the users with the help of a password harvesting feature.
Cerber – This type of attack is done by sending a malicious email file to the user, which affects the system of the user.
With this type of attack, the hacker steals the user’s information and uses it to get money as a ransom from the user to release his credentials — this type of malware saw an increase with the rise of Cryptocurrency.
RaaS – RaaS stands for Ransomware-as-a-Service. This type of malware attack is used by hackers to make money by hacking and selling user’s data to other criminals who make such malicious software and transmit them via emails, spammy links, etc.
These are the most used cyber-attacks by hackers in today’s world.
Emotet – It was once a banking Trojan, but the bot has evolved as a full-scale threat making it the most prevalent malware of 2019.
Botnets—Botnets can be used to perform DDOS attacks, through which the attacker can access the user’s device and connection.
Botnets can also be used to steal a user’s data or send spammy emails. They can also target different types of devices. Self-organizing botnet swarms are expected to continue in 2019.
Cryptomining Malware—Attackers prefer this type of malware due to the increase in cryptocurrency transactions worldwide.
Cryptomining is a way to harness the power of a large number of computers and other electronic devices. An attacker can make money by executing a cryptojacking attack on the user.
Because of this, experts say that Cryptomining will be present in 2019 as well. So Just Be Aware!!!
Conclusion
As cybercriminals continuously seek to make money from untapped sources, malware will increase.
With the increase in transactions using cryptocurrency, there is an increase in the number of malware attacks on users from their operating systems, and once the malware is deployed, it keeps sending the user’s valuable information to the hacker.
The best way to stay out of all this is by keeping yourself and your system updated regarding malware. Hope this blogs helps!
Recommended For You:

